Hyperbolic angle
Categories: hyperbolic functions

In this article we will look at the hyperbolic functions sinh and cosh. We will see why they are called hyperbolic functions, how they relate to sine and cosine, and why the parameter of the sinh and cosh functions can be considered to represent an angle.
The hyperbolic functions
The sinh function is defined as:
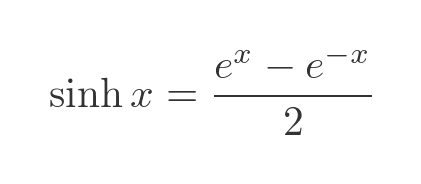
The cosh function is defined as:
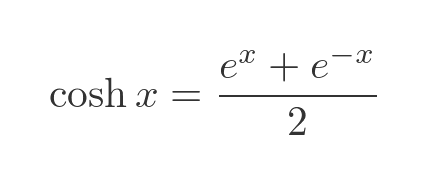
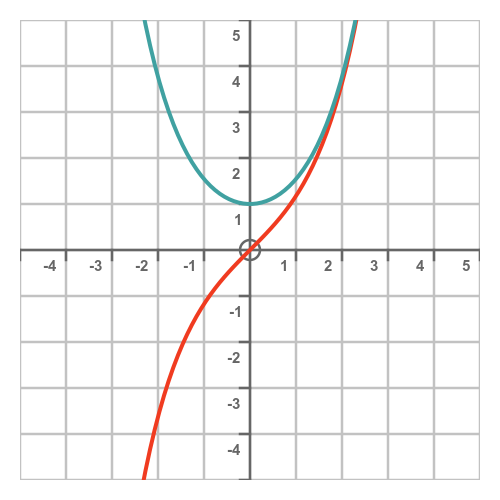
The graph of the 2 functions looks like this (sinh in red, cosh in cyan):
Sine and cosine make a circle
We can create a parametric equation based on the cosine and sine functions, using the parameter t, like this:
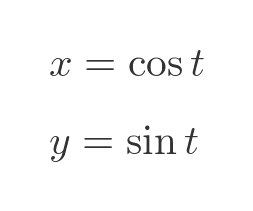
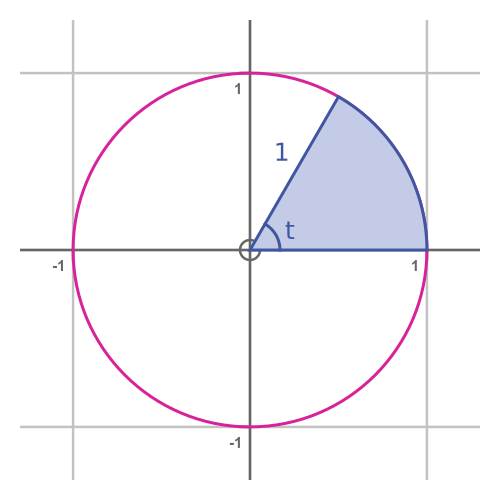
The parametric equations define a curve. For some value t, the curve will pass through the point P, with coordinates (cos t, sin t):
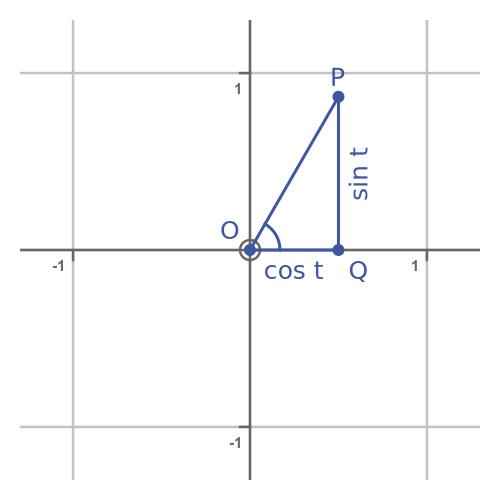
From the Pythagorean identity we can see that OP is equal to 1 for any value of t:
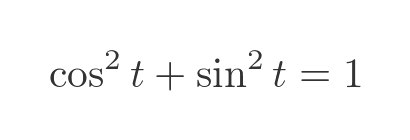
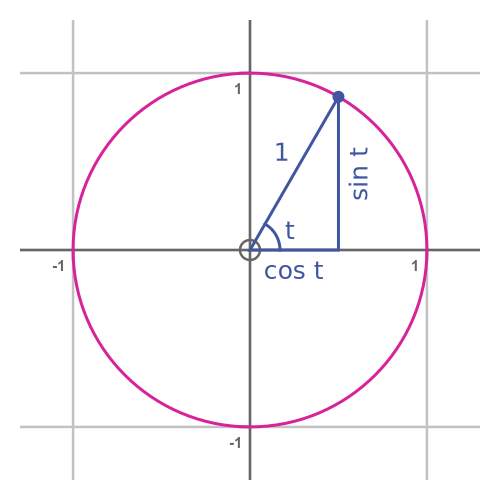
This tells us that the parametric equations describe a unit circle. It is also clear from basic trigonometry that the angle at the centre is equal to the parameter t:
An alternative way to prove that the curve is a circle is to replace cos t with x, and sin t with y (from the parametric equation above). This gives us the standard formula for a unit circle:
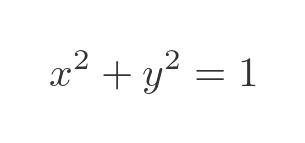
There is another useful fact we can derive about this parametric curve. The area of the sector is equal to t/2 (when t is measured in radians, of course):
This follows since the total angle in a circle is 2π, so the area on the sector as a fraction of the total circle area is:
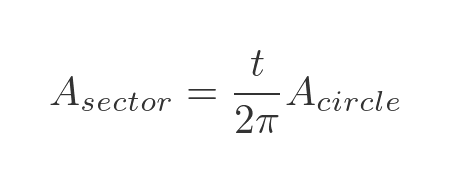
And since the total area of a unit circle is π, the area of the sector is:
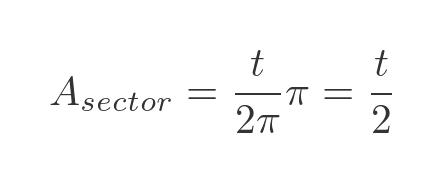
sinh and cosh make a hyperbola
Now let's look at a different system of parametric equations, based on the hyperbolic functions:
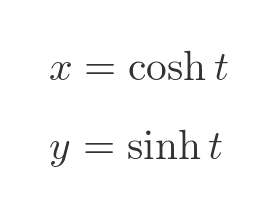
We can take various values of t, and plot the resulting (x, y) values on a graph:
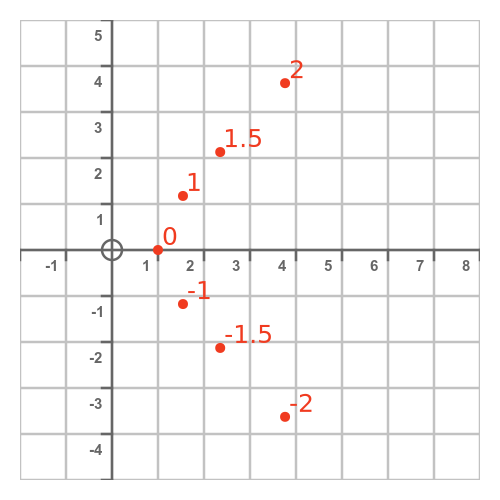
If we repeat this for every point, we get a curve like this:
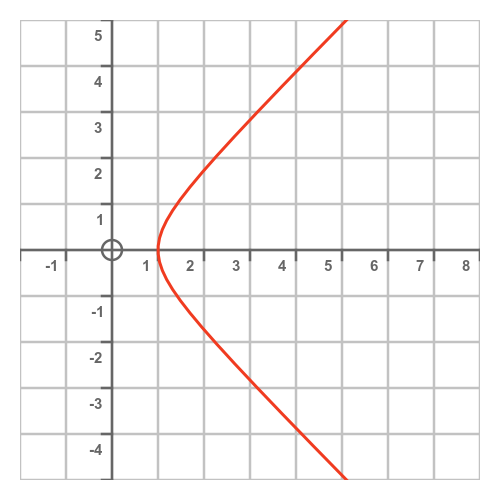
This curve is a hyperbola. More precisely, it is the unit rectangular hyperbola. We can see this quite easily using the following identity of the hyperbolic functions:
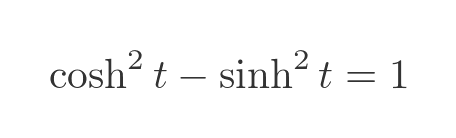
Substituting x and y, just like we did for the circle case, gives:
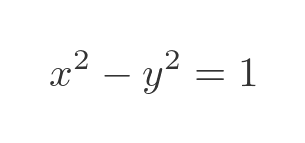
This is, indeed, the formula for the unit rectangular hyperbola.
The circle and hyperbola as conic sections
If we plot a unit circle and a unit hyperbola on the same graph, it looks like this:
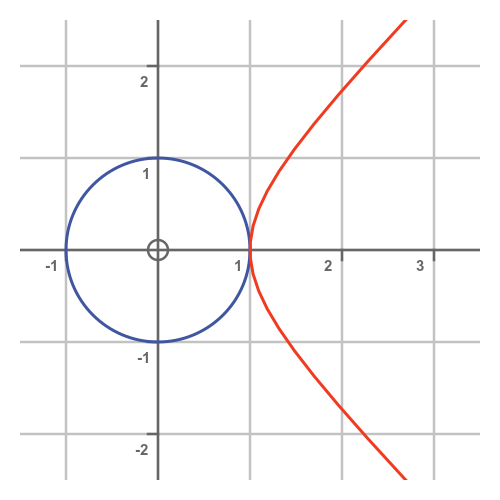
The two graph touch at the point (1, 0).
We can gain further insight into the relationship by viewing these two shapes as conic sections. A conic section is a shape that is formed when a plane cuts through a cone. In our case, we will use a specific cone where the sides are at an angle of 45 degrees to the vertical centre line of the cone.
We can cut the cone with a horizontal plane, like this:
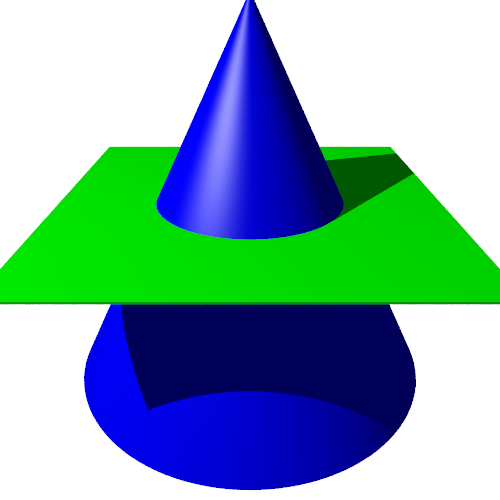
This creates a circular section:
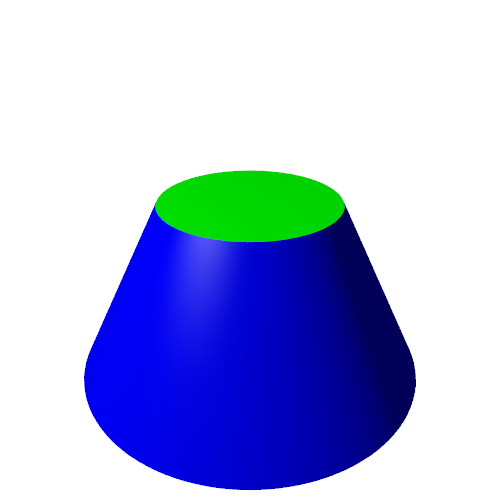
If we place the horizontal plane at a distance of 1 unit below the tip of the cone, the circle will have a radius of 1 (note that this is only true because we specified that the cone has an angle of 45 degrees).
We can also cut the cone with a vertical plane, like this:
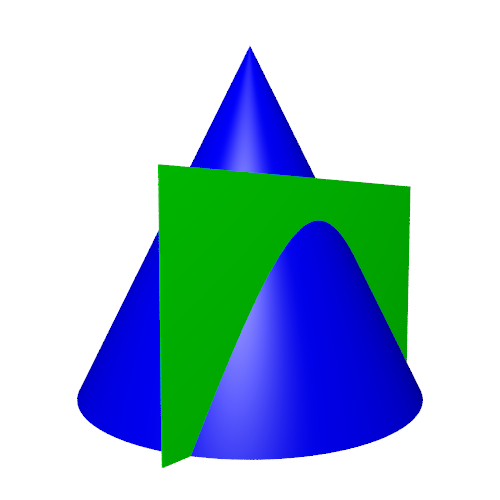
This creates a hyperbolic section. We have rotated the view so our viewpoint is perpendicular to the cut plane (i.e. we are looking directly at the cut plane):
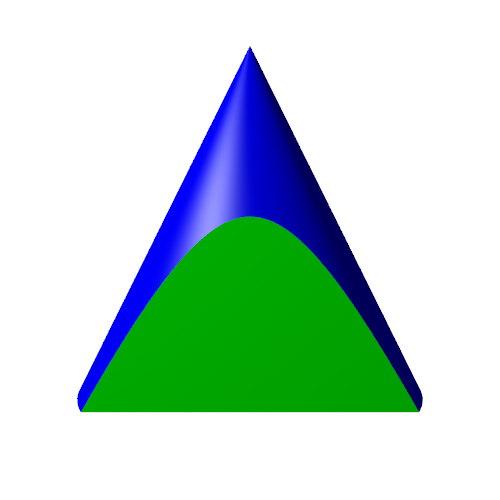
If we ensure that the vertical plane is 1 unit away from the centre line of the cone, this will be a unit hyperbola (again, this is only true because we specified that the cone has an angle of 45 degrees). If we cut the cone both vertically and horizontally, it looks like this:
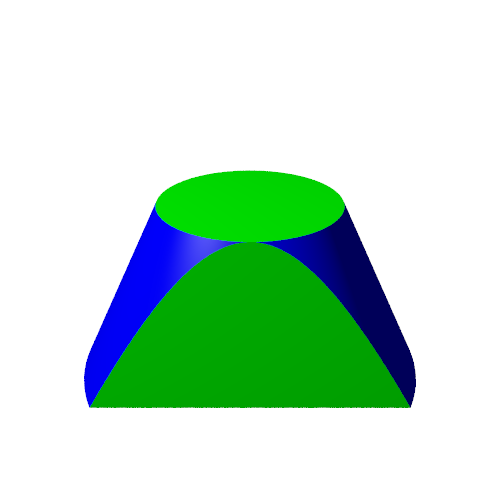
The circle and hyperbola touch at one point. This point is the equivalent of the point (1, 0) on the graph of the circle and hyperbola from earlier.
The hyperbolic angle
We previously looked at a sector of a circle formed by the x-axis, and a radius of the circle that passes through the point (cos t, sin t). We noted that this radius also makes an angle t with the x-axis and that the area of the sector is t/2:

We can draw an analogous "sector" on a unit hyperbola:
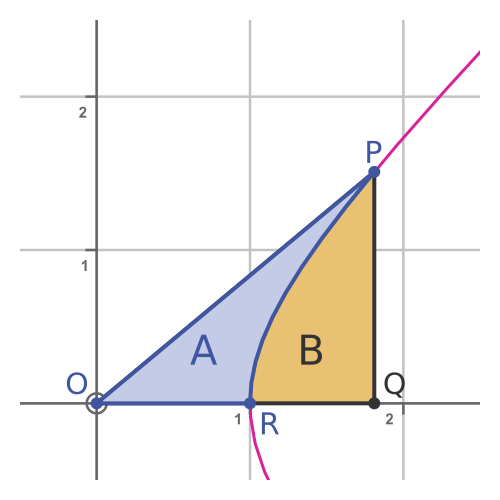
We are interested in the blue region A, formed by the almost triangular shape ORP. As we will see shortly, this region has an area equal to t/2 where t defines the point P. The point P is (cosh t, sinh t).
We call t the hyperbolic angle because it relates to the area of the sector in the same way as the angle t in the previous circular case.
Note, however, that the angle ROP is not equal to t. That relationship will be the subject of a future article.
Proof of hyperbolic angle
We will finish off by proving that the area A is equal to t/2. We will do this by first finding the combined area of A and B (which is the triangle OPQ), then finding area B by integration, then finally finding area A by subtraction.
We will use a few standard identities of the hyperbolic functions. These are easily proved using the exponential form of the sinh and cosh, and multiplying out, but we will take this as read in the proof below to keep it a bit shorter.
Finding the area of A plus B
We know that point P is (cosh t, sinh t), so the triangle OPQ has width cosh t and height sinh t. Its area is therefore:
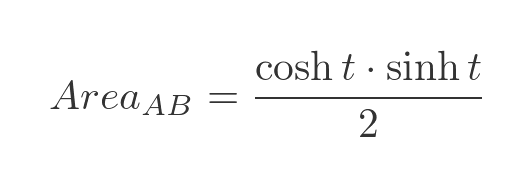
We will use a standard identity for the product of sinh and cosh:
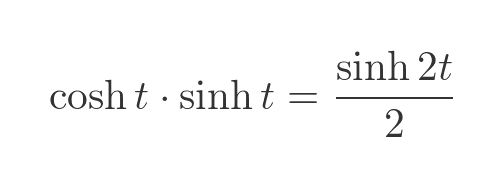
Dividing by 2 gives us the final area in terms of 2t, which will be useful later:
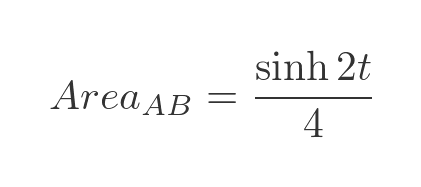
Finding area B
The area B is the area under the curve between R (where x = cosh 0) and Q where x = cosh t*. Now we know that the curve is a hyperbolic curve with the equation:
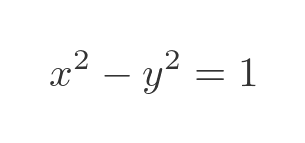
This can be rearranged as:
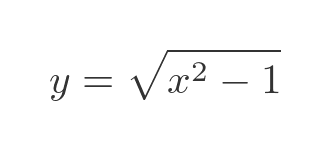
We can see from the diagram that we are interested in the positive root. So let's integrate this to find area B. The region B is bounded by x values of cosh 0 and cosh t:
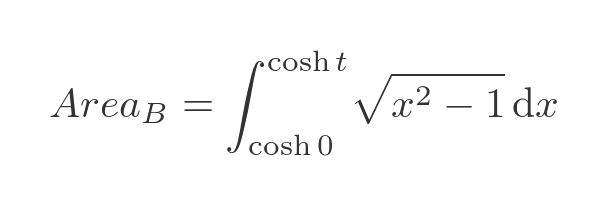
We will now integrate this by substitution, using:
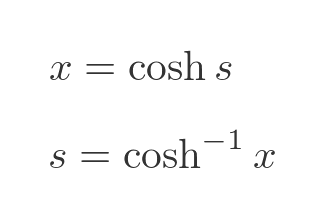
Which means:
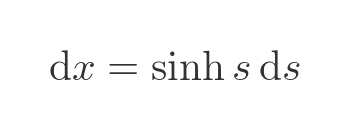
Our integral can now be written like this (notice the range, in terms of s, is 0 to t):
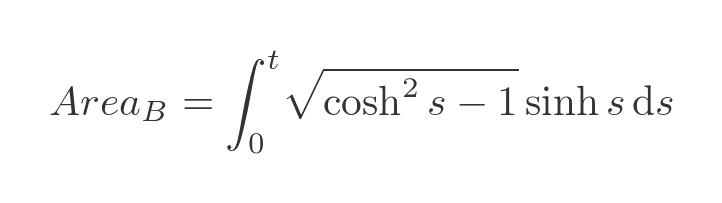
We can use another standard identity, and again we are only interested in the positive root:
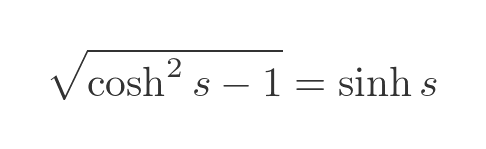
This simplifies our integral to:
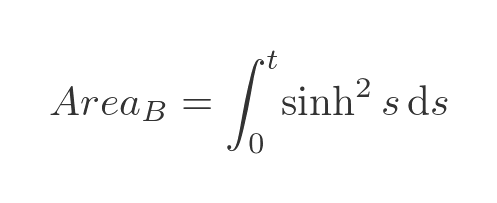
This is a standard integral, which can be found in various tables online. The indefinite integral is given by:
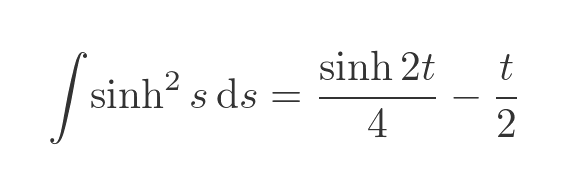
Area B is given by the definite integral between s = 0 and s = t:
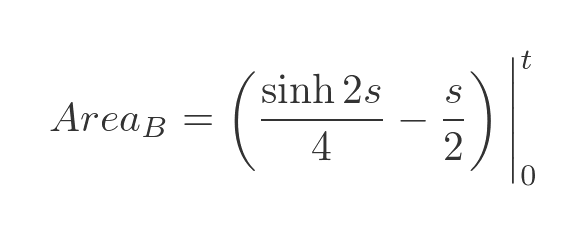
When t = 0, both terms evaluate to 0. So the final result is:
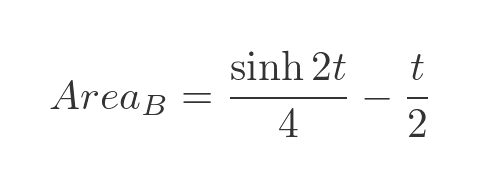
Finding area A
If we take the previous expression for the area of A and B:
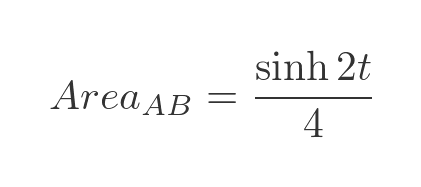
And subtract the value we just obtained for the area of B, we get the area of A:
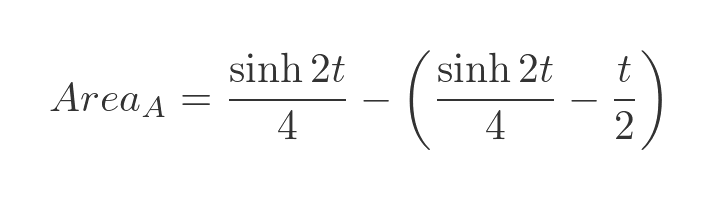
Which simplifies to:
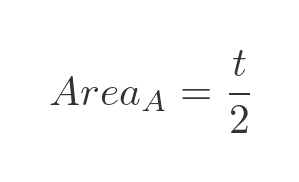
So the area of the sector is equal to half the hyperbolic angle, t.
See also

Join the GraphicMaths Newletter
Sign up using this form to receive an email when new content is added:
Popular tags
adder adjacency matrix alu and gate angle answers area argand diagram binary maths cartesian equation chain rule chord circle cofactor combinations complex modulus complex polygon complex power complex root cosh cosine cosine rule cpu cube decagon demorgans law derivative determinant diagonal directrix dodecagon eigenvalue eigenvector ellipse equilateral triangle euler eulers formula exercises exponent exponential exterior angle first principles flip-flop focus gabriels horn gradient graph hendecagon heptagon hexagon horizontal hyperbola hyperbolic function hyperbolic functions infinity integration by parts integration by substitution interior angle inverse hyperbolic function inverse matrix irrational irregular polygon isosceles trapezium isosceles triangle kite koch curve l system line integral locus maclaurin series major axis matrix matrix algebra mean minor axis n choose r nand gate newton raphson method nonagon nor gate normal normal distribution not gate octagon or gate parabola parallelogram parametric equation pentagon perimeter permutations polar coordinates polynomial power probability probability distribution product rule proof pythagoras proof quadrilateral questions radians radius rectangle regular polygon rhombus root sech segment set set-reset flip-flop sine sine rule sinh sloping lines solving equations solving triangles square standard curves standard deviation star polygon statistics straight line graphs surface of revolution symmetry tangent tanh transformation transformations trapezium triangle turtle graphics variance vertical volume volume of revolution xnor gate xor gate