Rules of exponents
Categories: exponentials

This article looks at exponents and the exponential function.
Here is a video:
What are exponential functions
An exponential function in x takes the form a raised to the power x, that is $a^x$. a is called the base, and x is called the exponent.
Here are the first few powers of a:
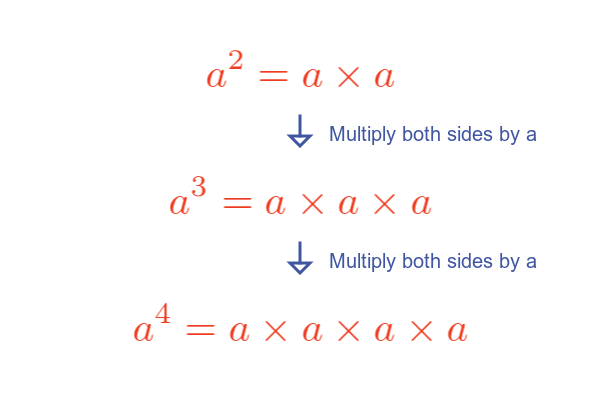
$a^2$, of course, is commonly called a squared and is calculated as a multiplied by a.
$a^3$ is commonly called a cubed and is calculated as a multiplied by a multiplied by a.
$a^4$ doesn't have a special name, it can be called the fourth power of a, or a to the power four.
Simple definition of the exponential function
Generally, $a^n$, where n is an integer of 2 or greater is the nth power of a and is often described as a multiplied by itself n times.
That isn't quite true though. a squared is actually a multiplied by itself once, not twice.
A better definition would be that $a^n$ is one multiplied by a, n times.
Exponential values
If we chose a base of 2, we can calculate some values:
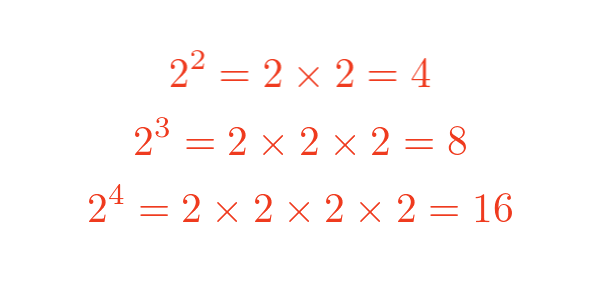
As another example, if we chose a base of 10, we can get different values:
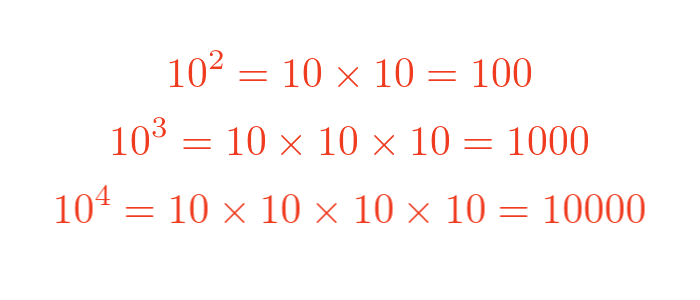
Laws of exponents
There are several laws that can be used to simplify expressions involving exponents:
- Product of powers rule.
- Quotient of powers rule.
- Power of a power rule.
- Power of a product rule.
- Power of a quotient rule.
Product of powers rule
When multiplying two exponential terms that have the same base, we add the exponents:
$$ a^p a^q = a^{p + q} $$
Here is an illustration for $a^3$ multiplied by $a^2$:
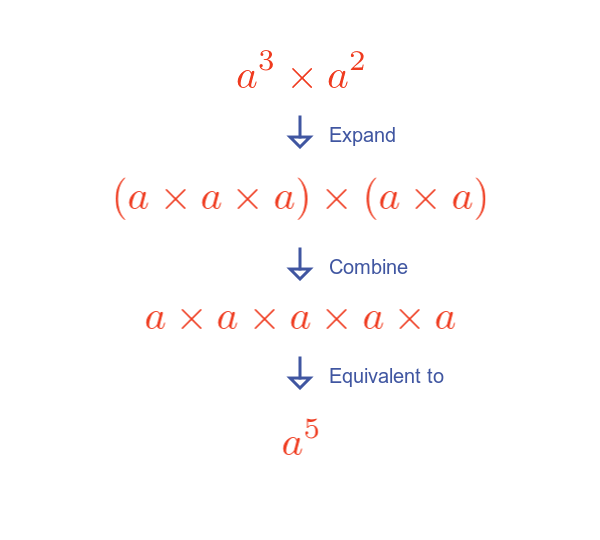
Expanding each term shows that the total number of terms is 5, the sum of the exponents.
Quotient of powers rule
When dividing two exponential terms that have the same base, subtract the exponent of the denominator from the exponent of the numerator:
$$ \frac{a^p}{a^q} = a^{p - q} $$
Here is an illustration for $a^5$ divided by $a^3$:
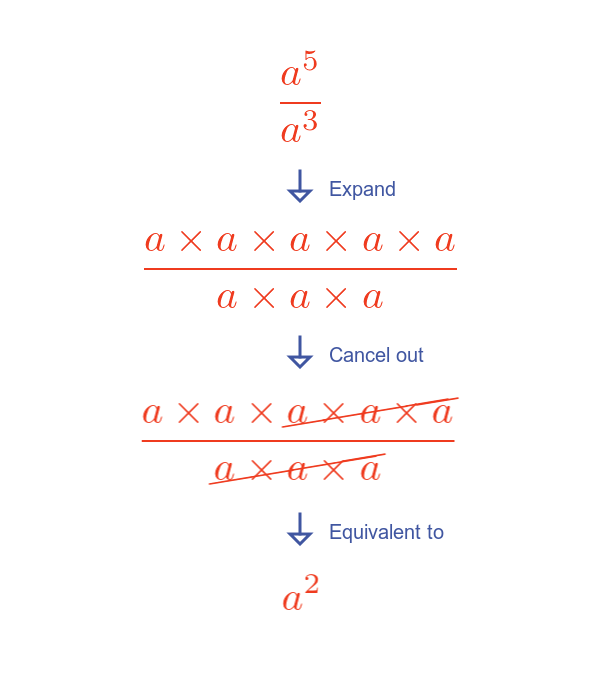
Expanding each term and cancelling top and bottom shows that the total number of terms is 2, the difference between the exponents.
Power of a power rule
When raising a power to a power, multiply the two exponents:
$$ {a^p}^q = a^{p q} $$
Here is an illustration for $a^3$ squared:
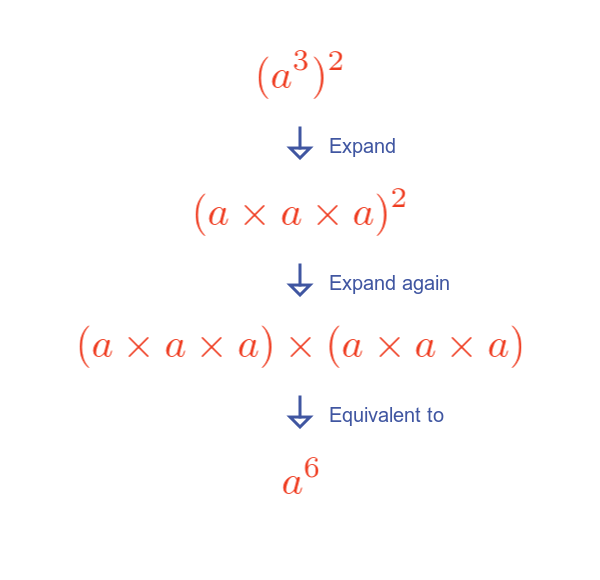
Expanding each term and cancelling top and bottom shows that the total number of terms is 6, the product of the exponents.
Power of a product rule
If we have a base that consists of a product of two (or more) terms, all raised to a power, we can simplify it by distributing the exponent to each term in the base:
$$ (a b)^p = a^p b^p $$
Here is an example of ab cubed:
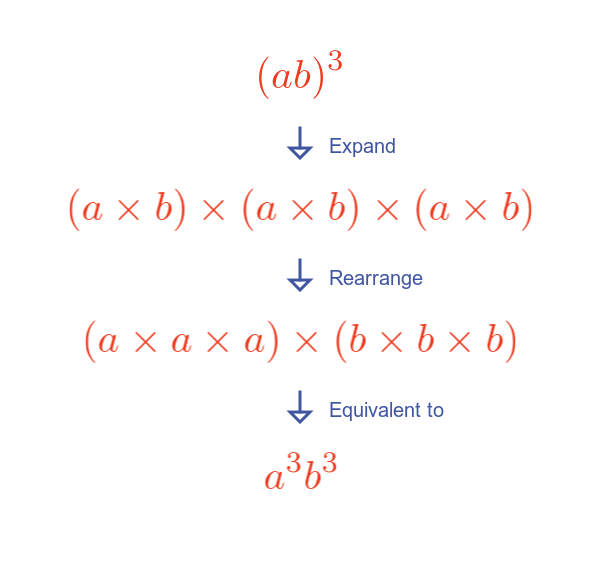
Expanding and rearranging the equation for ab cubed demonstrates the rule. This can easily be extended to other powers.
Power of a quotient rule
The previous rule also applies to the quotient of two values, all raised to a power. Again we can simplify it by distributing the power to each term in the quotient:
$$ (\frac{a}{b})^p = \frac{a^p}{b^p} $$
Here is an example of a/b cubed:
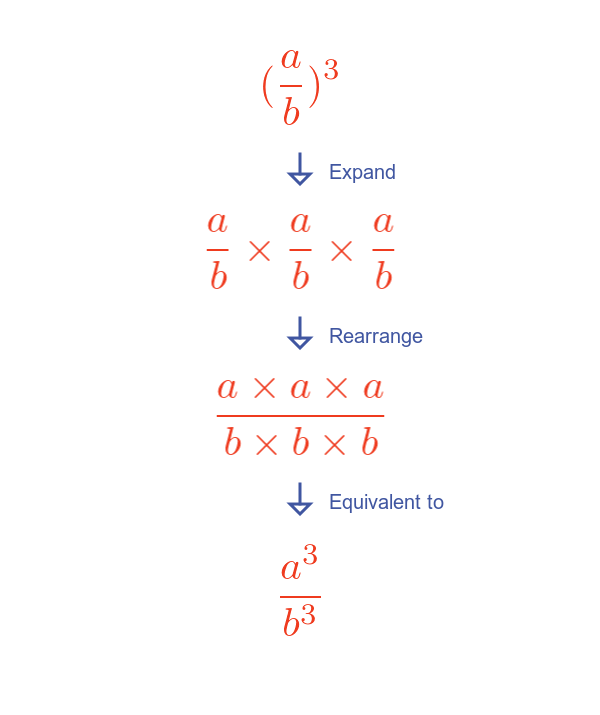
Expanding and rearranging the equation for a/b cubed demonstrates the rule. This can easily be extended to other powers.
See also

Join the GraphicMaths Newletter
Sign up using this form to receive an email when new content is added:
Popular tags
adder adjacency matrix alu and gate angle answers area argand diagram binary maths cartesian equation chain rule chord circle cofactor combinations complex modulus complex polygon complex power complex root cosh cosine cosine rule countable cpu cube decagon demorgans law derivative determinant diagonal directrix dodecagon eigenvalue eigenvector ellipse equilateral triangle euler eulers formula exercises exponent exponential exterior angle first principles flip-flop focus gabriels horn gradient graph hendecagon heptagon hexagon horizontal hyperbola hyperbolic function hyperbolic functions infinity integration by parts integration by substitution interior angle inverse hyperbolic function inverse matrix irrational irregular polygon isosceles trapezium isosceles triangle kite koch curve l system line integral locus logarithm maclaurin series major axis matrix matrix algebra mean minor axis n choose r nand gate net newton raphson method nonagon nor gate normal normal distribution not gate octagon or gate parabola parallelogram parametric equation pentagon perimeter permutations polar coordinates polynomial power probability probability distribution product rule proof pythagoras proof quadrilateral questions radians radius rectangle regular polygon rhombus root sech segment set set-reset flip-flop sine sine rule sinh sloping lines solving equations solving triangles square square root standard curves standard deviation star polygon statistics straight line graphs surface of revolution symmetry tangent tanh transformation transformations trapezium triangle turtle graphics uncountable variance vertical volume volume of revolution xnor gate xor gate