Geometry basic rules
Categories: gcse geometry

Here are some basic rules and definitions of geometry that are useful to know. They are also covered in this video:
Angles around a point
There are several geometry rules for angles.
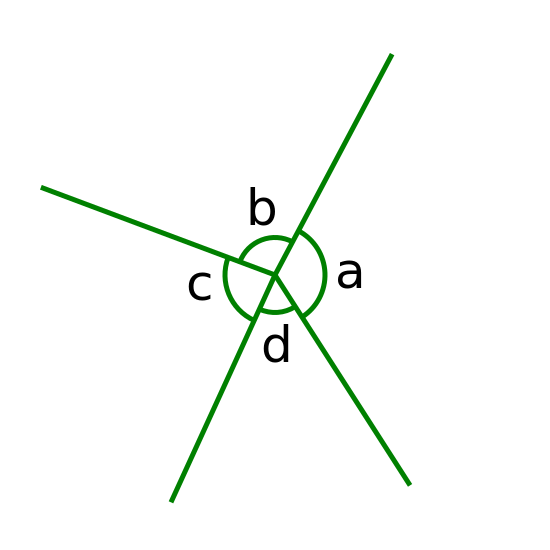
The angles around a point add up to 360°.
a + b + c + d = 360°
Angles on a line
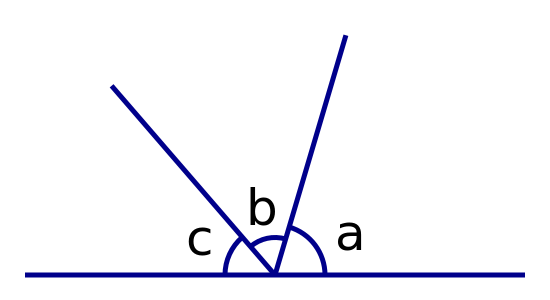
The angles on a straight line add up to 180°.
a + b + c = 180°
Angles in a triangle
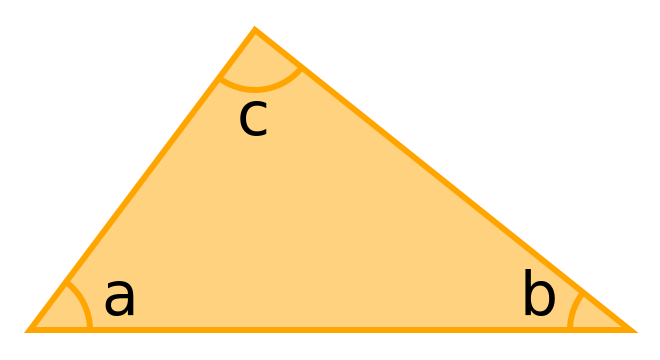
The interior angles in a triangle add up to 180°.
a + b + c = 180°
Angles in a quadrilateral
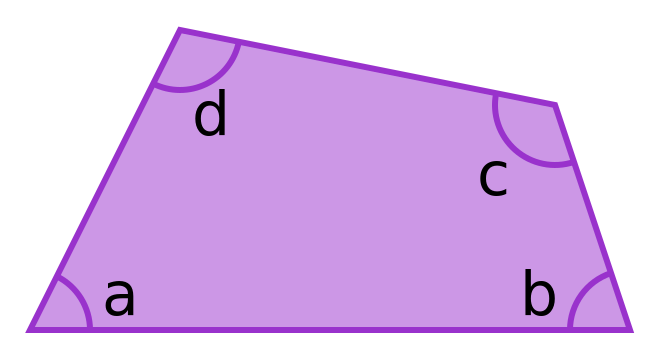
The interior angles in a quadrilateral (any 4-sided shape) add up to 360°.
a + b + c + d = 360°
Exterior angles of a triangle
There are a number of geometry rules for triangles.
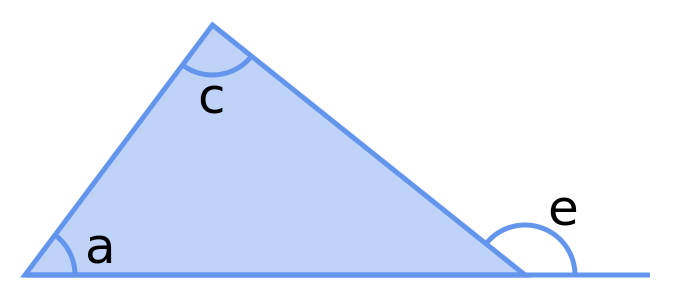
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the 2 opposite interior angles.
e = a + b
Angles and sides of an isosceles triangle
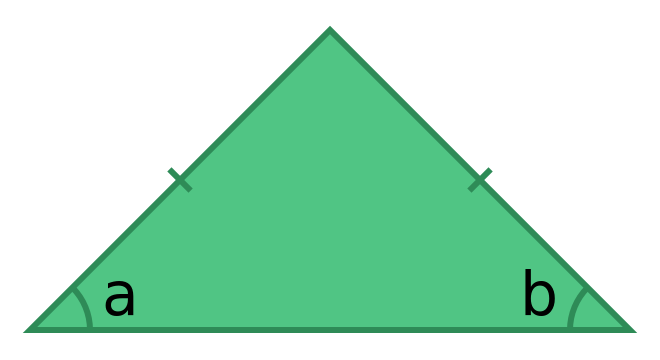
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length (the two sides indicated by the tick marks that are drawn across the lines). It also has two equakl angles:
a = b

Join the GraphicMaths Newletter
Sign up using this form to receive an email when new content is added:
Popular tags
adder adjacency matrix alu and gate angle area argand diagram binary maths cartesian equation chain rule chord circle cofactor combinations complex modulus complex polygon complex power complex root cosh cosine cosine rule cpu cube decagon demorgans law derivative determinant diagonal directrix dodecagon eigenvalue eigenvector ellipse equilateral triangle euler eulers formula exponent exponential exterior angle first principles flip-flop focus gabriels horn gradient graph hendecagon heptagon hexagon horizontal hyperbola hyperbolic function hyperbolic functions infinity integration by parts integration by substitution interior angle inverse hyperbolic function inverse matrix irrational irregular polygon isosceles trapezium isosceles triangle kite koch curve l system line integral locus maclaurin series major axis matrix matrix algebra mean minor axis nand gate newton raphson method nonagon nor gate normal normal distribution not gate octagon or gate parabola parallelogram parametric equation pentagon perimeter permutations polar coordinates polynomial power probability probability distribution product rule proof pythagoras proof quadrilateral radians radius rectangle regular polygon rhombus root sech set set-reset flip-flop sine sine rule sinh sloping lines solving equations solving triangles square standard curves standard deviation star polygon statistics straight line graphs surface of revolution symmetry tangent tanh transformation transformations trapezium triangle turtle graphics variance vertical volume of revolution xnor gate xor gate